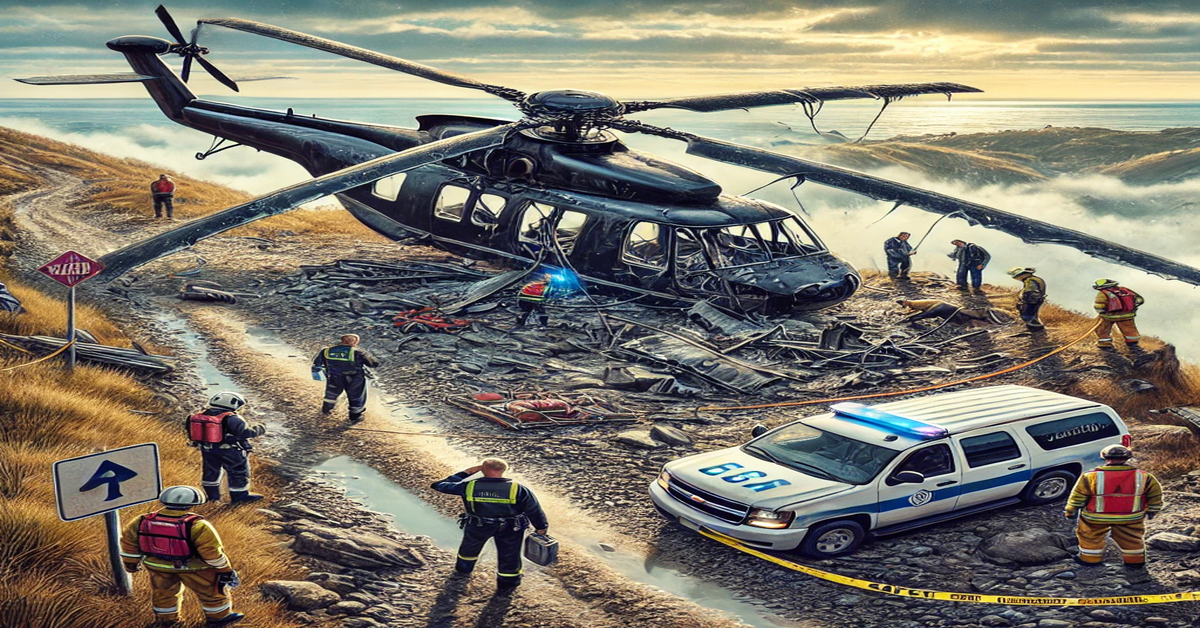
Helicopter crashed are versatile and widely used aircraft known for their ability to take off, hover, and land vertically. From military operations to medical emergencies and leisure travel, helicopters play a vital role across various industries. However, when a helicopter crashes, it often makes headlines due to the potential for severe consequences. Understanding the causes, prevention measures, and overall impact on aviation safety is crucial for both aviation professionals and the general public.
This article delves into the key aspects of helicopter crashes, including common causes, major accidents in history, the importance of safety regulations, and advancements in technology designed to reduce the likelihood of such incidents. We also explore the psychological and financial impacts of helicopter crashes and conclude with frequently asked questions (FAQs) that address common concerns.
Common Causes of Helicopter Crashes
1. Pilot Error
Pilot error is one of the leading causes of helicopter crashes. It can result from:
- Poor decision-making during adverse weather conditions.
- Miscommunication between crew members.
- Inadequate training or fatigue.
When pilots fail to respond correctly to emergencies or overlook pre-flight checks, the risk of accidents increases significantly.
2. Mechanical Failure
Mechanical issues are another major factor in helicopter crashes. Components that commonly fail include:
- Rotors: Any damage to the main or tail rotor can be catastrophic.
- Engines: Engine malfunctions due to lack of maintenance or manufacturing defects.
- Hydraulics: Loss of hydraulic power can cause pilots to lose control.
Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to mitigate the risks of mechanical failure.
3. Adverse Weather Conditions
Helicopters are particularly sensitive to weather conditions, including:
- Heavy rain, fog, or snow that reduces visibility.
- Strong crosswinds that destabilize flight.
- Icing that affects rotor performance.
Flying in adverse weather requires advanced pilot training and the use of sophisticated navigation equipment.
4. Bird Strikes and External Obstacles
Collisions with birds or obstacles such as power lines, trees, or buildings can lead to accidents. Bird strikes are especially dangerous during takeoff and landing phases.
5. Air Traffic Control and Communication Issues
In busy airspace, communication breakdowns between pilots and air traffic controllers can result in mid-air collisions or loss of spatial awareness.
Major Helicopter Crashes in History
1. Kobe Bryant’s Helicopter Crash (2020)
On January 26, 2020, a Sikorsky S-76B helicopter carrying NBA star Kobe Bryant, his daughter, and seven others crashed in Calabasas, California. The cause was determined to be pilot disorientation due to poor visibility in foggy weather.
2. Super Puma Helicopter Crash (2009)
A Eurocopter AS332 Super Puma crashed into the North Sea, killing 16 people. Investigations revealed mechanical failure in the gearbox as the primary cause.
3. Chinook Helicopter Crash (1986)
A British Royal Air Force Chinook helicopter crashed on the Mull of Kintyre, killing 29 people. Pilot error and inadequate navigation systems were cited as contributing factors.
These incidents highlight the multifaceted nature of helicopter crashes, emphasizing the need for continuous improvements in safety.
Safety Regulations and Protocols
Aviation authorities worldwide have implemented strict safety regulations to minimize the risk of helicopter crashes. The following protocols are essential in enhancing overall safety:
1. Pre-Flight Inspections
Comprehensive pre-flight checks ensure that mechanical components, navigation systems, and communication devices are functioning properly. Pilots and maintenance crews follow detailed checklists to verify the airworthiness of the aircraft.
2. Pilot Training and Certification
Pilots undergo rigorous training that includes simulation-based exercises, emergency maneuvers, and weather navigation. Periodic re-certification ensures that pilots maintain their competency.
3. Maintenance and Repairs
Scheduled maintenance, as mandated by aviation authorities, ensures that helicopters are free from mechanical defects. Any parts showing signs of wear and tear are replaced immediately.
4. Weather Monitoring and Flight Planning
Advanced weather monitoring tools and flight planning systems help pilots avoid hazardous conditions. Ground control teams also play a crucial role in guiding helicopters through safe flight paths.
5. Air Traffic Management
Improved air traffic control systems reduce the risk of mid-air collisions. Controllers use radar, GPS, and real-time data to guide pilots and manage airspace efficiently.
6. Emergency Response Preparedness
Training pilots and crew members on emergency procedures can save lives. Emergency locator transmitters (ELTs) and life-saving equipment onboard improve survival rates during crashes.
Technological Advancements Reducing Helicopter Crashes
1. Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS)
These systems provide pilots with real-time alerts about potential ground collisions. By using terrain databases and GPS, EGPWS can prevent controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) accidents.
2. Flight Data Monitoring Systems
Modern helicopters are equipped with black boxes that record flight data. Analyzing this data helps identify patterns that could lead to accidents and allows operators to implement preventive measures.
3. Automated Flight Controls
Autonomous or semi-autonomous flight control systems assist pilots during critical situations, reducing human error.
4. Weather Radar and Anti-Icing Systems
Advanced weather radar systems provide real-time information about turbulence and precipitation, allowing pilots to make informed decisions. Anti-icing systems prevent the buildup of ice on critical components.
5. Collision Avoidance Systems
Helicopter crashed are now equipped with collision avoidance systems that detect nearby aircraft and provide alerts to avoid mid-air collisions.
Psychological and Financial Impacts of Helicopter Crashes
Psychological Impacts
- Survivors: Survivors of helicopter crashes often experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and depression.
- Families of Victims: The sudden loss of loved ones can lead to prolonged grief and emotional trauma.
- First Responders: Those who arrive at crash sites may experience emotional distress due to the nature of the incidents.
Financial Impacts
- Operators: Airlines or companies operating helicopters may face lawsuits, increased insurance premiums, and reputational damage.
- Manufacturers: If mechanical failure is identified, manufacturers may face costly recalls and litigation.
- Victim Compensation: Governments and organizations often provide compensation to victims’ families, adding to the financial burden.
Prevention Strategies and Best Practices
1. Investing in Advanced Pilot Training
Ongoing pilot training programs that include handling adverse weather and emergency situations are essential for reducing crashes.
2. Implementing Predictive Maintenance
Using sensors and data analytics to predict component failures before they occur can help avoid mechanical breakdowns.
3. Strengthening Communication Protocols
Ensuring seamless communication between pilots, air traffic controllers, and ground crews reduces the risk of misunderstandings.
4. Deploying Advanced Navigation Systems
Equipping helicopters with state-of-the-art navigation tools ensures better situational awareness and safer flight paths.
5. Enhancing Safety Audits
Regular safety audits by aviation authorities and independent inspectors help identify potential risks and enforce compliance.
Conclusion
Helicopter crashed, though relatively rare compared to other forms of transportation accidents, have a significant impact due to their potential for catastrophic outcomes. Understanding the common causes, implementing strict safety regulations, and embracing technological advancements are key to minimizing these incidents. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, the focus on improving pilot training, enhancing maintenance procedures, and deploying cutting-edge technologies will be crucial in ensuring safer helicopter operations worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is the most common cause of helicopter crashes?
The most common cause is pilot error, often due to poor decision-making, fatigue, or inadequate training. Mechanical failure and adverse weather conditions are also significant factors.
2. How can pilot training help prevent helicopter crashes?
Rigorous training programs teach pilots to handle emergencies, adverse weather, and communication challenges, reducing the likelihood of crashes.
3. Are helicopters more dangerous than airplanes?
Helicopters are generally considered more sensitive to weather and mechanical issues due to their design, but strict regulations and advancements in technology have made them safer over time.
4. What role does maintenance play in helicopter safety?
Regular maintenance and inspections are critical to detecting and addressing mechanical issues, ensuring that helicopters remain airworthy.
5. What technologies are available to reduce helicopter crashes?
Technologies like Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems, weather radar, collision avoidance systems, and automated flight controls play a crucial role in reducing crashes.
6. What should passengers do to increase their safety during helicopter flights?
Passengers should follow the safety instructions provided by the crew, wear seatbelts, and be aware of emergency procedures. Choosing operators with good safety records is also recommended.